Introduction

As a small business owner in 2025, navigating the complex landscape of tax planning can feel overwhelming. With recent changes in tax laws and evolving business conditions, it’s more important than ever to have a solid tax strategy that helps you keep more of your hard-earned money while staying compliant with IRS regulations. In this article we discussed proven tax saving strategies for small business owners in 2025. Learn how to legally reduce your tax burden, maximize deductions, and optimize your business structure for tax efficiency.
Understanding the Current Tax Landscape
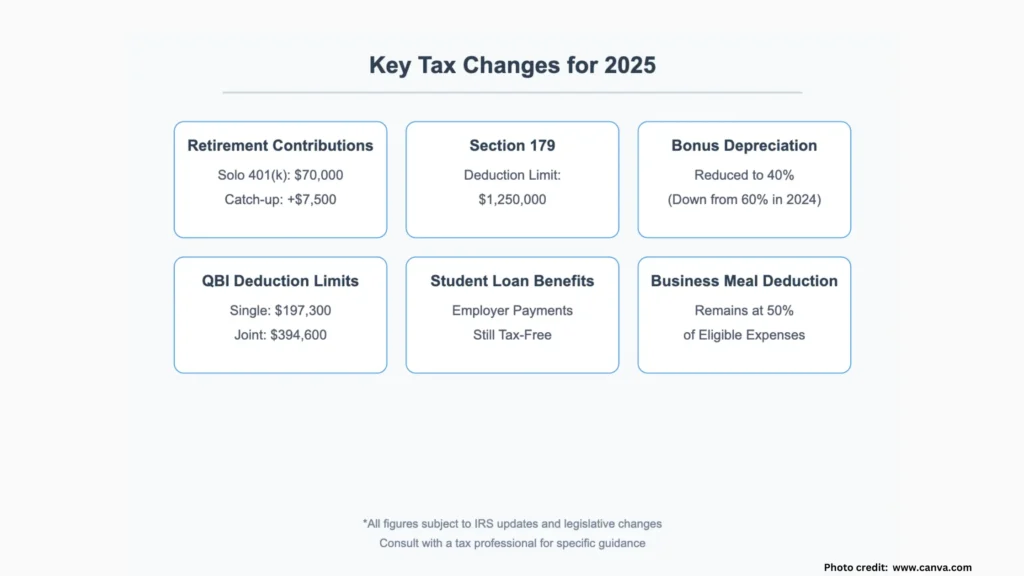
Key Tax Changes for 2025
Several important changes affect small business owners this year:
- Bonus depreciation reduced to 60% (down from 80% in 2023)
- Standard business meal deduction returned to 50% (down from 100% during COVID-19)
- Updated tax brackets and increased standard deductions
- Modified retirement plan startup credits
- Changes to pass-through entity taxation in multiple states
Essential Tax Saving Strategies for 2025
1. Optimize Your Business Structure
Your choice of business structure significantly impacts your tax obligations. Consider these options:
- Sole Proprietorship: Simple but comes with self-employment tax burden
- LLC: Flexible taxation options with liability protection
- S-Corporation: Potential savings on self-employment taxes
- C-Corporation: Flat 21% corporate tax rate, but double taxation on dividends
Pro tip: Regularly review your business structure as your income grows. Many businesses benefit from transitioning from sole proprietorship to S-corporation status when profits exceed $40,000-50,000 annually.
2. Maximize Qualified Business Income Deduction
The Section 199A deduction allows eligible businesses to deduct up to 20% of qualified business income. For 2025, this applies to:
- Single filers with taxable income under $191,950
- Joint filers with taxable income under $383,900
3. Strategic Equipment and Asset Purchases
For 2025, take advantage of the 60% bonus depreciation before it decreases further. Consider:
- Section 179 expensing: Deduct up to $1,220,000 in qualifying equipment purchases
- Strategic timing of major purchases
- Vehicle deductions with specific limits for luxury automobiles
- Technology upgrades and office equipment
Real-world example: A small manufacturing company purchased $200,000 in new equipment in early 2024, immediately deducting 60% ($120,000) through bonus depreciation, significantly reducing their tax liability.
4. Optimize Retirement Planning
Retirement plans offer dual benefits of tax savings and future security:
- Solo 401(k): Contribute up to $69,000 in 2024 ($70,000 in 2025)
- SEP IRA: Save up to 25% of income or $69,000 (2024)
- Traditional and Roth IRA combinations
- Additional $7,500 catch-up contributions for those 50 and older
Tax saving opportunity: Small business owners can potentially save over $20,000 in taxes annually through strategic retirement contributions.
5. Health Insurance and Benefits Planning
Maximize health-related tax benefits:
- Self-employed health insurance deduction
- Health Savings Accounts (HSAs)
- Health Reimbursement Arrangements (HRAs)
- Qualified Small Employer Health Reimbursement Arrangements (QSEHRAs)
6. Employee-Related Tax Strategies

Smart employment strategies can reduce your tax burden:
- Hire family members strategically
- Implement accountable plans for employee reimbursements
- Utilize work opportunity tax credits
- Offer tax-advantaged fringe benefits
- Consider contractor vs. employee classifications carefully
Expert insight: “One of the most overlooked strategies is implementing an accountable plan for employee reimbursements. This can save both the employer and employees significant tax dollars while providing necessary business expense coverage.” – Abraham Nnanna
7. Home Office and Business Expense Optimization
Maximize deductions through careful documentation:
- Home office deduction: $5 per square foot up to 300 square feet
- Vehicle expenses: 67 cents per mile in 2024
- Travel and entertainment expenses
- Professional development and education costs
- Insurance premiums and business-related fees
8. Strategic Income and Expense Timing
Implement smart timing strategies:
- Defer income to future tax years when advantageous
- Accelerate deductible expenses
- Bunch deductions when beneficial
- Manage accounts receivable timing
- Plan major purchases around fiscal year end

9. Debt and Financing Strategies
Optimize your business financing for tax efficiency:
- Deduct business loan interest
- Consider equipment financing timing
- Evaluate lease vs. purchase decisions
- Utilize business credit cards strategically
- Structure owner loans properly
10. State and Local Tax Planning
Consider multi-state tax implications:
- Pass-through entity tax elections in 35 states
- State-specific credits and incentives
- Nexus considerations for remote work
- Sales tax compliance strategies
- State-specific depreciation rules
Key consideration: Many states offer specific incentives for small businesses. For example, some states provide additional credits for creating jobs or investing in designated economic zones.
11. Green Energy and Sustainability Tax Incentives
Take advantage of environmental tax benefits:
- Electric vehicle credits for business vehicles
- Solar and renewable energy installations
- Energy-efficient building improvements
- Sustainable equipment upgrades
- Carbon footprint reduction incentives
2024 Update: The Inflation Reduction Act provides nearly $400 billion in green energy incentives that small businesses can leverage for tax savings.
READ ALSO: 11 Bitcoin Tax Havens: Escape the Crypto Tax Crunch in 2024
12. Technology and Digital Transformation Credits
Invest in technology while saving on taxes:
- Software development credits
- Cybersecurity improvements
- Digital transformation initiatives
- Cloud computing investments
- Research and development credits
Advanced Tax Planning Strategies
Creating a Comprehensive Tax Strategy
Develop a year-round approach:
- Regular Tax Planning Meetings
- Quarterly review of financials
- Annual strategy updates
- Cash flow projections
- Tax liability estimates
- Documentation Systems
- Digital receipt management
- Expense tracking software
- Mileage logging apps
- Time tracking for tax purposes
- Professional Team Assembly
- CPA or tax advisor
- Business attorney
- Financial planner
- Insurance specialist
- Payroll professional
Risk Management and Compliance
Protect your business while maximizing savings:
- Regular audit preparation
- Internal controls implementation
- Record retention policies
- Tax deadline management
- Estimated tax payment planning
Industry-Specific Considerations
Different industries have unique tax-saving opportunities:
Service-Based Businesses
- Professional liability insurance deductions
- Home office opportunities
- Contract labor management
- Educational expense deductions
Retail Businesses
- Inventory management strategies
- Point-of-sale system deductions
- Employee discount programs
- Shrinkage and loss deductions
Manufacturing Businesses
- Equipment depreciation
- Raw material costs
- Energy efficiency credits
- Research and development
Common Tax Planning Mistakes to Avoid
- Poor Record Keeping
- Missing Deadline Dates
- Incorrect Business Structure
- Overlooking Available Credits
- Mixing Personal and Business Expenses
Best Practices for Implementation
Creating Your Tax Planning Calendar
- January-March
- Gather previous year’s tax documents
- Review Q1 estimated tax payments
- Implement new year tax strategies
- April-June
- Complete previous year’s tax returns
- Mid-year strategy review
- Update profit projections
- July-September
- Review Q3 estimated tax payments
- Plan end-of-year purchases
- Evaluate tax bracket position
- October-December
- Year-end tax planning
- Strategic income/expense timing
- Plan for next year
Working with Tax Professionals
Choosing the Right Tax Professional
Look for:
- Relevant small business experience
- Industry-specific knowledge
- Proactive communication style
- Year-round availability
- Technology integration capabilities
- Continuing education commitment
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Investment in professional tax planning typically provides returns through:
- Maximized deductions
- Reduced audit risk
- Strategic business decisions
- Time savings
- Peace of mind
Conclusion
Effective tax planning for small business owners in 2025 requires a comprehensive, year-round approach. By implementing these strategies, maintaining proper documentation, and working with qualified professionals, you can significantly reduce your tax burden while maintaining compliance with all regulations.
Key Takeaways
- Start tax planning early and maintain consistent efforts throughout the year
- Regularly review and adjust your business structure and strategies
- Take advantage of available deductions and credits
- Maintain meticulous records and documentation
- Invest in professional guidance when needed
Next Steps
- Review your current tax strategy
- Schedule a consultation with a tax professional
- Implement a robust documentation system
- Create a tax planning calendar
- Regular strategy reviews and updates
Remember, tax planning is not a one-time event but an ongoing process that requires regular attention and updates. Stay informed about tax law changes and work with qualified professionals to ensure your business maintains optimal tax efficiency while remaining compliant with all regulations.
This comprehensive guide provides a solid foundation for small business tax planning in 2025. However, tax laws and regulations can change, so always consult with qualified tax professionals for advice specific to your situation.
FAQ Section
Q: How much should a small business set aside for taxes?
A: While it varies by business structure and income level, most small businesses should set aside 25-30% of their net income for taxes. This includes federal, state, and self-employment taxes.
Q: Can I still take advantage of 100% bonus depreciation in 2024?
A: No, bonus depreciation has decreased to 60% for 2024. It will continue to decrease by 20% each year until it phases out completely in 2027.
Q: How do I know if I should change my business structure for tax purposes?
A: Consider consulting a tax professional when your annual profit consistently exceeds $40,000-50,000, or if you’re paying significant self-employment taxes. They can help analyze whether a different structure would be more tax-efficient.
Q: What are the most commonly overlooked tax deductions for small businesses?
A: Common overlooked deductions include:
- Bank and credit card processing fees
- Professional development and education costs
- Business insurance premiums
- Local business licenses and permits
- Professional membership dues
- Business startup costs
- Website and digital marketing expenses
Q: How does the Qualified Business Income deduction work in 2024?
A: The QBI deduction allows eligible business owners to deduct up to 20% of their qualified business income. Income thresholds for 2024 are $191,950 for single filers and $383,900 for joint filers. Above these thresholds, the deduction may be limited or eliminated based on business type and income level.
Q: What documentation do I need to maintain for tax purposes?
A: Essential documentation includes:
- All receipts and invoices
- Bank and credit card statements
- Vehicle mileage logs
- Asset purchase and sale records
- Employee and contractor records
- Business meeting notes
- Travel expense documentation
- Home office measurements and expenses
In another related article, Cryptocurrency Taxes: Understanding Your Tax Obligations




